Melanoma
Understanding Melanoma: A Critical Concern
Melanoma is a particularly dangerous form of skin cancer that originates in melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. While melanocytes are primarily located in the skin, they can also be found in areas such as the eyes and bowel, though the risk of developing melanoma in these non-skin areas is significantly lower.
Although melanoma is less common than other types of skin cancer, it is the most lethal, accounting for about 75% of all skin cancer-related deaths. In the United States alone, approximately 160,000 new cases of melanoma are diagnosed each year. Excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, whether from the sun or tanning beds, is a major risk factor for developing melanoma.
The Importance of Early Detection and Regular Skin Exams
Early detection is crucial when it comes to treating melanoma, and regular Total Body Skin Exams (TBSEs) by a dermatologist play a vital role in this process. Dermatologists are trained to spot suspicious moles, lesions, or skin changes that may indicate melanoma. In addition to professional screenings, self-examinations are equally important. Individuals should routinely check their skin for any changes in the shape, size, or color of moles, as well as the appearance of new spots.
Combining professional dermatological evaluations with regular self-exams significantly increases the likelihood of catching melanoma early, when it is most treatable. Prompt intervention can greatly improve treatment outcomes, making regular skin checks a key component of maintaining overall skin health.
At Dermatology Affiliates, your skin health is our top priority. Our expert providers are dedicated to guiding you and your loved ones through every step of your skin wellness journey, ensuring the best possible care and outcomes.
Examples of Melanoma
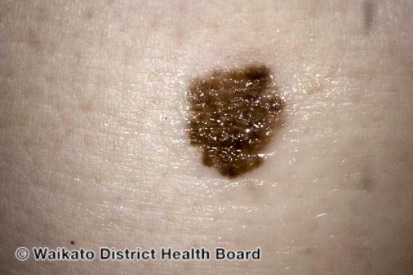
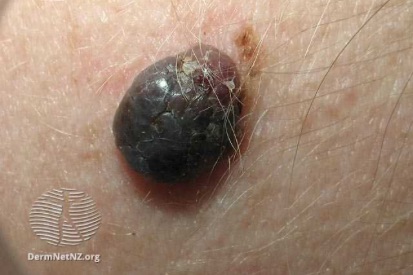
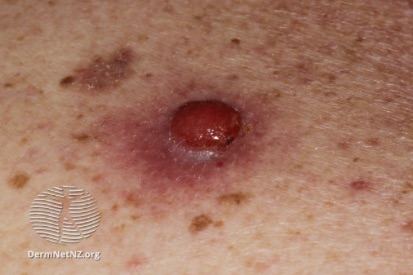
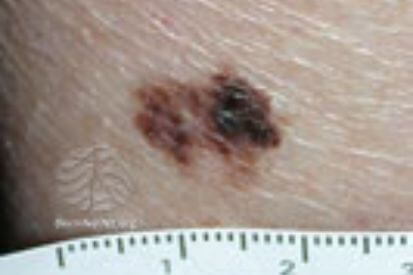
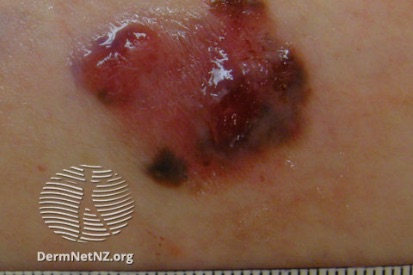
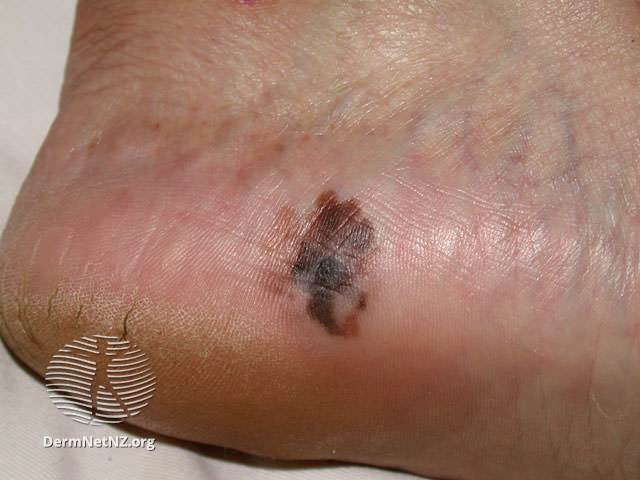
Symptoms of Melanoma
- Melanoma most often presents itself with the change of an existing mole, including change of symmetry, color, or shape.
- Irregular mole borders – scalloped, wavy, or notched.
- Diameter - anything new growing in size.
- Moles that itch, ooze or bleed.
- Melanoma can appear on normal skin tissue and does not always start as a mole.
What Causes Melanoma?
- Melanoma is primarily caused by the uncontrolled growth of pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) in the skin.
- Melanoma is often triggered by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or tanning beds.
- Genetic factors and a history of severe sunburns also contribute to the development of melanoma.
How to Prevent Melanoma
Frequently Asked Questions: Melanoma
The leading cause of melanoma is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, whether from sunlight or tanning beds. Additional risk factors include fair skin, a history of sunburns, having numerous moles, and a family history of melanoma.
Diagnosis typically involves a biopsy, where a sample from the suspicious area is removed and examined under a microscope. Dermatologists often apply the ABCDE rule—Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variations, Diameter over 6mm, and Evolution or change—to determine if a mole may be melanoma.
Melanoma is classified into stages 0 through IV, with stage 0 representing melanoma in situ, confined to the top layer of the skin, and stage IV indicating that the cancer has metastasized to other organs. The staging process is crucial for determining the severity of the disease and plays a key role in guiding treatment decisions.
Accurate staging allows dermatologists to tailor treatment plans to the patient's specific condition, improving the likelihood of successful outcomes and helping to predict prognosis.
Treatment options for melanoma depend on the stage of the cancer and may include surgical excision, lymph node removal, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy. The choice of treatment is individualized based on factors such as the patient's overall health and the characteristics of the melanoma.
Yes. A skin check performed by a dermatologist involves a thorough examination of the skin to identify any abnormalities, including moles, lesions, or other signs of skin conditions or skin cancer. Regular skin checks are essential for early detection and management of skin issues, and, skin cancer.
From Our QualDerm Family of Brands: Melanoma Treatment Options
Melanoma Treatment Options
We will confirm melanoma through a biopsy and pathological examination and then treat appropriately.
Treatment options for melanoma provided by a dermatologist may include surgical procedures to remove the cancerous tissue, such as excision or Mohs surgery. Additionally, your dermatologist may recommend therapies like immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy, depending on the stage and characteristics of the melanoma. Close monitoring, regular skin checks, and collaboration with other specialists ensure effective treatment and reduce the risk of recurrence.
If you notice unusual growths on your skin as mentioned above, we highly recommend scheduling an appointment with one of our providers. Annual skin checks are essential for early detection.
Early detection and treatment are crucial elements of comprehensive skin cancer care.
Featured Blogs

- General Dermatology
As the U.S. population ages, the number of Americans who suffer from skin diseases will continue to rise, according to the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD).
Read More
- Skin Cancer
- General Dermatology
- Sun Safety
A person will get sunburned from spending time outside without sunscreen and sun-protective clothing. Read to learn more about the dangerous effects of sunburn.
Read More
- Skin Cancer
- General Dermatology
- Sun Safety
A skin cancer story shared by a Dermatology Affiliates employee. Learn how easy it is for skin cancer to sneak into your life in many ways.
Read MoreFeatured Products for Sun Protection
Check your local office for current stock!
Check your local office for current stock!


