Folliculitis
Superficial Folliculitis affects the upper part of the hair follicle and can cause clusters of red bumps, pus-filled blisters, red and/or inflamed skin, as well as itchiness or tenderness.
Deep Folliculitis is a more serious type of folliculitis that starts deeper in the skin surrounding the hair follicle and thus can infect the whole hair follicle. Deep folliculitis can manifest as a large swollen bump and pus-filled blisters and can cause pain and possible scarring once the infection has disappeared.
If you're dealing with the discomfort of folliculitis, our trusted Dermatology Affiliates providers offer specialized care, providing effective solutions to alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence. Schedule an appointment at Dermatology Affiliates for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized folliculitis management to promote healthy skin.
Examples of Folliculitis
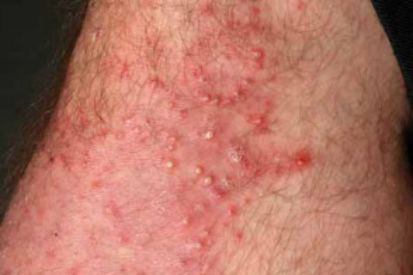
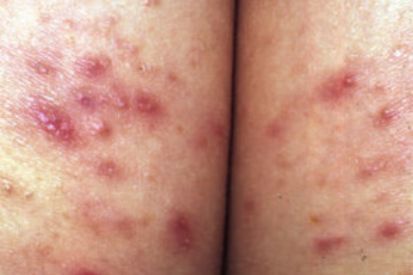
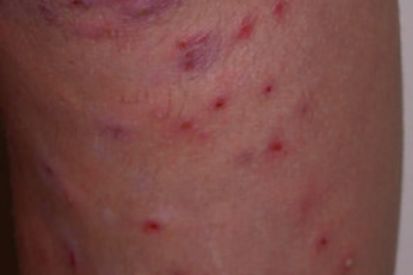
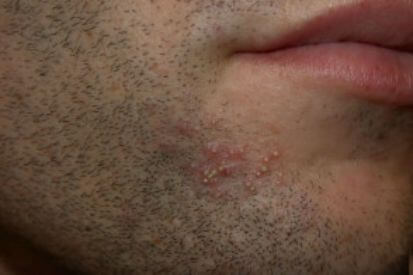
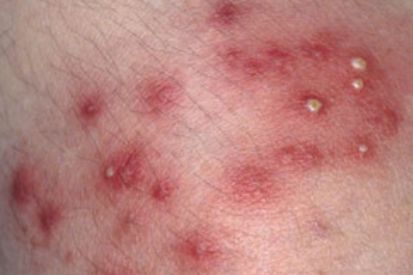
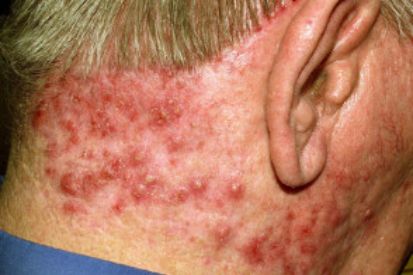

What are the Symptoms of Folliculitis?
Folliculitis can cause discomfort and irritation, affecting areas where hair follicles become inflamed or infected. If you're experiencing the following folliculitis symptoms, Pinnacle Dermatology can offer expert care to diagnose and treat a hair follicle infection.
- Itchy or painful bumps around hair follicles
- Clusters of red bumps or pus-filled blisters
- Red, inflamed, or tender skin
- Persistent itchiness or soreness
- Possible scarring after the infection clears
Causes of Folliculitis
Certain lifestyle factors and skin conditions can increase the risk of developing this hair follicle infection, leading to discomfort and potential complications. Understanding these causes is essential for preventing folliculitis and reducing flare-ups. Common causes of folliculitis may include:
- Shaving, which can cause irritation or ingrown hairs
- Friction from tight clothing
- Excessive sweating, especially in humid conditions
- Skin inflammation from underlying conditions like eczema
- Skin injuries that allow bacteria to enter the follicles
- Non-breathable materials, such as adhesive tape on the skin
- Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections
How to Prevent Folliculitis
- Gentle Shaving Techniques: Use a sharp, clean razor and shave in the direction of hair growth with minimal pressure to reduce irritation.
- Maintaining Skin Hygiene: Cleanse the skin regularly with mild, fragrance-free soap to remove potential irritants and bacteria.
- Avoiding Tight Clothing: Wear loose, breathable fabrics to minimize friction and allow the skin to breathe.
- Proper Wound Care: Treat cuts, scrapes, or skin injuries promptly to prevent bacterial infections that may lead to folliculitis.
- Hydration and Moisturization: Keep the skin well-hydrated with dermatologist-recommended moisturizers to maintain a strong skin barrier.
Folliculitis FAQs
Your dermatologist can diagnose folliculitis by examining the affected area. Sometimes, they may perform a culture or other tests to identify the specific microorganism causing the issue.
Folliculitis itself is usually not contagious, but the microorganisms responsible can be transmitted through direct contact. Maintaining good hygiene and avoiding the sharing of personal items can help prevent the spread of infection.
Yes, specific activities or jobs that involve extended exposure to hot and humid conditions, friction, or contact with contaminated surfaces can elevate the risk of developing folliculitis. Athletes, frequent shavers, and individuals in certain occupations may be more prone to this condition.
Yes, folliculitis can develop on any area of the body that has hair follicles. Commonly affected regions include the face, neck, chest, back, buttocks, and thighs. The location and severity of folliculitis can differ from person to person, depending on factors like skin type, hair texture, and exposure to irritants.
Moisturizers can help manage folliculitis, especially if dry or irritated skin is a contributing factor. Using a gentle, non-comedogenic moisturizer can maintain skin hydration, reduce irritation, and support the skin's barrier function, potentially easing symptoms. However, moisturizers may not treat the underlying cause, particularly if folliculitis is due to a bacterial or fungal infection, in which case specific treatments prescribed by a dermatologist are necessary. Opt for fragrance-free, non-comedogenic products to minimize further irritation, and consult with a dermatologist for a tailored treatment plan.
From our QualDerm Family of Brands: Skin Moisturizing Tips
Folliculitis Treatment
Common treatment modalities include:
- Topical Antibiotics or Antifungals: For mild cases, we may prescribe topical antibiotics or antifungal creams to target the bacterial or fungal infections causing folliculitis.
- Oral Medications: In more severe or recurrent cases, oral antibiotics or antifungal medications may be recommended to treat the infection from within.
- Corticosteroids: Topical or oral corticosteroids help alleviate inflammation, reducing redness and itching associated with folliculitis.
- Laser Therapy: Our dermatologists may use laser therapy to target and destroy hair follicles, preventing further outbreaks of chronic or recurrent folliculitis.
Featured Blogs
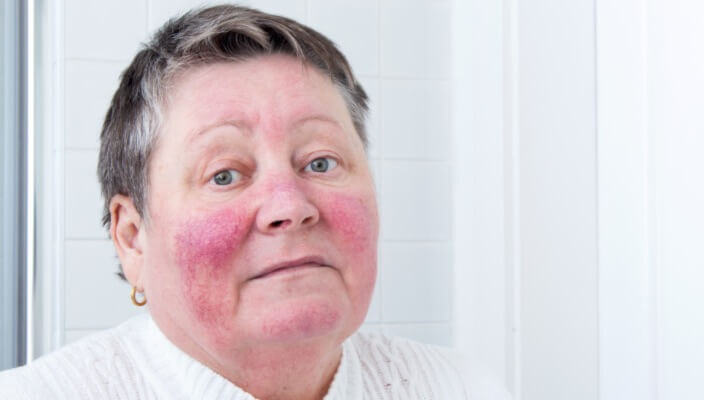

- General Dermatology
- Chronic Skin Conditions
Your dermatologist or dermatology PA can help you treat your rosacea and reverse the damage it has caused.
Read More
- Skin Care
- Botox
- Cosmetic Treatments
Retiniods are proven to combat fine lines, brown spots and improve texture, “tret” has been shown to enhance collagen production, even skin tone, unclog pores, and smooth skin texture.
Read More
- Skin Care
- Cosmetic Treatments
The cosmetic treatment “microneedling” has created quite a buzz in the beauty industry as a restorative skin treatment. Now, its rejuvenating abilities extend to the scalp too.
Read MoreFeatured Products
Check your local office for current stock!
Check your local office for current stock!


